Description
There are three ways to search for a record in Dynamics 365[1]:
- Single entity Quick Find - the search bar on the top right of a view.
- Multi-entity Quick Find or Categorized Search - available from the Search icon in the navigation bar.
- The Relevance Search – also available from the Search icon in the navigation bar.
The Relevance Search is similar to the Categorized Search, because it can also search for trough multiple entities. Categorized search displays result per entity, with one list for each entity. With Relevance Search, there is only one list, with all entities mixed. But results are sorted by their relevance with the search and matches are highlighted in the list.
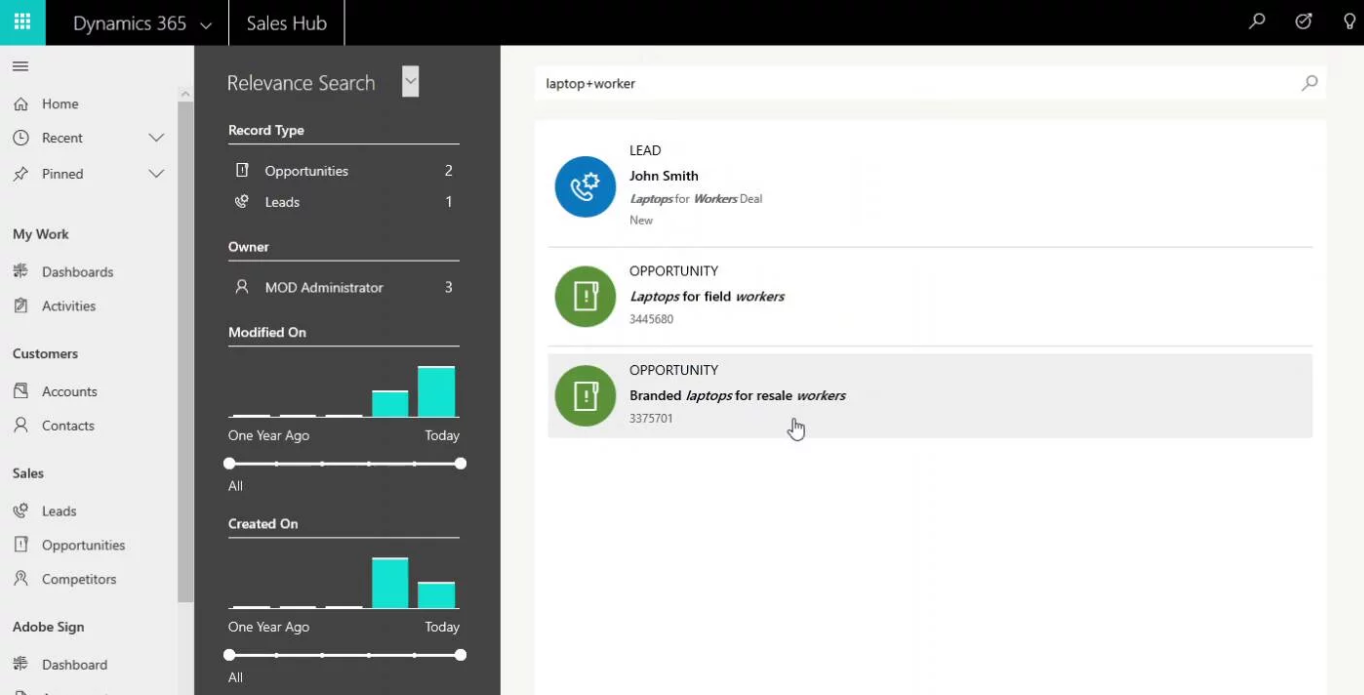
In the list, records are represented with six fields:
- An icon related to the record

- The type of entity (e.g: CONTACT)
- The OOB field “Name” of the record
- Four fields related to the entity. Those fields will be sorted out by the relevance to the search, with matches being highlighted.
Relevance Search offers Facets, accessible on the left of the result list. Facets enable to filter down the results with a user-friendly interface. It’s possible to filter the results to a specific entity via the facets: the list and the facets will be refresh.
Behind the scenes, Relevance Search uses Azure Search Index[2]. This means that the data enabled to be searchable via the Relevance Search are sent with an external system. Therefore, Relevance Search is disabled by default. When enabled for the first time, a full synchronization will be made: it can take up to an hour to be finished. After that, any change in the data may take up to 15 minutes to appear in the search service.
Relevance Search can also look for text in documents attached to a Note, Email, or an Appointment in Dynamics 365.
It also makes usage of a natural language analyzer to break down words and produce better results. For example, a search for “ran” will match the words “run” and “running”.
Configuration
The System Administrators can also select the entities that are required for search by clicking on “Entities” and the “Configure Relevance Search” button from the solution window. The list of all entities will be displayed and administrators can select which ones will be available for the Relevance Search.
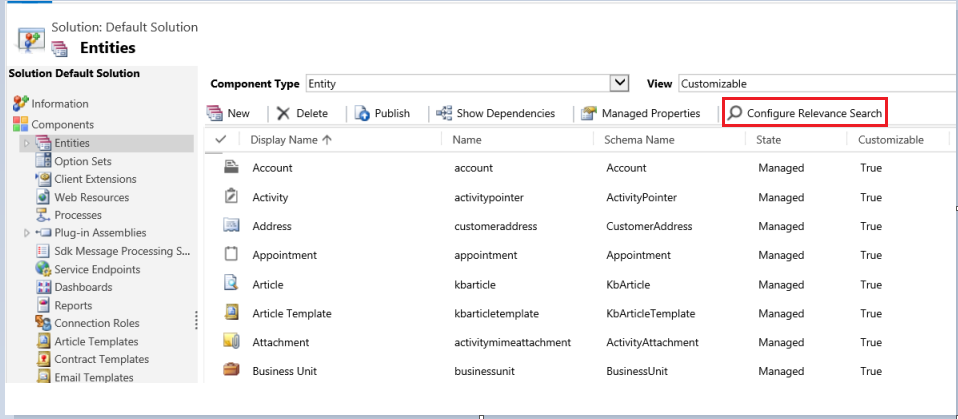
Once an entity has been enabled for Relevance Search, administrators need to choose upon which fields the search will be performed. Find Columns on a Quick Find View of an entity that define the searchable fields.
The Quick Find view is also used to define which fields appear as facets. At any time, only four fields can be shown as facets.
Take-away Points
Relevance search brings:
- Improved performance thanks to the external service Azure Search Index.
- Finds matches to any word in any field in the entity.
- Matches may include inflectional words (e.g: “Stream” -> stream, streaming, streamed).
- Matches are highlighted in the list
[1] Microsoft provides an article that compares the three searches.
[2] Azure Search Index is an online product contained in Azure. Therefore, Relevance Search is not available for on-premises organizations.